Gynecomastia can affect male patients at nearly any stage of life, sparking questions about its cause, appearance, and necessity for treatment. At the New Jersey Gynecomastia Center, we understand that age plays a powerful role in how and why this condition arises.
Whether a patient visits us as a parent wondering about adolescence, a young adult with new symptoms, or a man noticing changes later in life, it helps to recognize how gynecomastia differs with age. Understanding these differences will empower you to discuss your concerns confidently and consider the best next steps for your care.
Key Takeaways
Why Does Age Matter?
Gynecomastia describes the benign enlargement of breast gland tissue in males. This results from a hormonal imbalance between estrogen and testosterone, and can lead to swelling, tenderness, and a firmer texture under the nipple.
Age significantly influences both the causes and course of gynecomastia. For example, hormonal surges often cause adolescent cases, while medication or health changes drive the condition later in life. Understanding the particular age group helps our surgical team identify what causes gynecomastia and tailor care effectively.
The age at onset can also predict whether the condition will resolve on its own or require intervention.
Gynecomastia in Childhood and Infancy
Early-Onset Gynecomastia
Some infants show temporary breast tissue enlargement, which can be surprising for new parents. This form of gynecomastia usually results from exposure to maternal hormones during pregnancy. In nearly all cases, it resolves completely within a few weeks or months as hormone levels stabilize.
Prepubertal Gynecomastia
When gynecomastia develops before puberty in boys, it may persist longer and warrants evaluation. Medical conditions affecting hormones, such as genetic syndromes or hormone-producing tumors, can occasionally be factors. Our doctor at the New Jersey office will take a thorough history and examine your child for any signs requiring further investigation.
While rare, persistent or unexplained cases should prompt discussion with a qualified provider.
Gynecomastia in Adolescence: The Most Common Phase
Most cases of gynecomastia occur during puberty, often between ages 10 and 16. Testosterone and estrogen fluctuate dramatically during this transition, causing temporary tissue growth in up to two-thirds of boys. The tissue usually appears under the nipple, sometimes on both sides, causing sensitivity or discomfort.
Key Features of Adolescent Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia in teenagers most often appears gradually and without associated serious symptoms. This type usually resolves without intervention within several months to two years as hormone levels normalize. However, larger or persistent cases sometimes remain, affecting self-image and confidence at a sensitive time.
As a result, our team finds that adolescent males and their parents frequently seek advice regarding whether to wait or consider treatment options.
Emotional Impact during Adolescence
Adolescence brings challenges with self-esteem, peer interaction, and body image. Gynecomastia can heighten these struggles, especially if symptoms become noticeable under clothing or during athletic activities. Our surgeon emphasizes the importance of open, honest conversation with both the adolescent patient and family to provide supportive, age-appropriate care.
If the tissue remains after two years or is emotionally distressing, medical or surgical options can be considered to restore comfort and confidence.
Gynecomastia in Early and Middle Adulthood
For men in their twenties through forties, persistent or new gynecomastia often arises for distinctly different reasons than in adolescence. By these years, hormone levels generally stabilize, so our New Jersey team often investigates other causes.
Common Causes in Adults
Several factors can lead to gynecomastia in adult males. Our surgeon evaluates for the following:
- Medications: Prescription drugs such as anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, certain antidepressants, and heart medications sometimes cause breast enlargement.
- Substance use: Alcohol, marijuana, heroin, and some bodybuilding supplements are known contributors.
- Chronic health issues: Conditions like liver or kidney disease disrupt hormone metabolism, sometimes leading to gynecomastia.
- Hormonal disorders: Rarely, issues such as low testosterone production, pituitary gland diseases, or thyroid abnormalities are responsible.
Evaluating Adult Patients
At our practice, we closely review medication use, health conditions, and any new symptoms. Adult men often report only gradual changes or mild discomfort, while in some cases, the growth occurs rapidly or is tender. The condition may signal underlying medical issues, which is why our team may initiate further testing or refer you to a specialist for a complete workup.
Determining the exact trigger allows our doctor to recommend targeted treatment and helps prevent recurrence.
Gynecomastia in Older Adults
Enlargement of male breast tissue also becomes more prevalent with age, especially after age 50. Hormonal shifts continue throughout life, and the risk of gynecomastia increases with declining testosterone and rising relative estrogen.
Age-Related Factors in Later Life
- Andropause: Male hormone levels gradually decrease with age, increasing the imbalance that triggers gynecomastia.
- Medication use: Older adults tend to use more medications, some of which (such as heart or prostate drugs) commonly promote breast tissue growth.
- Chronic diseases: Health conditions requiring long-term treatment, such as cancer, heart failure, or kidney disease, often raise risk as well.
- Weight gain: Accumulation of body fat boosts estrogen, further increasing the likelihood of breast tissue enlargement.
Our surgeon approaches evaluation in seniors by considering both age-related changes and ongoing health needs, so that any underlying medical issues are addressed alongside gynecomastia treatment.
How Gynecomastia Progresses by Age
Gynecomastia changes in presentation, prognosis, and response to treatment depending on the age of onset. The timeline from first symptoms to resolution or stabilization also varies substantially.
Stages of Gynecomastia
- Acute phase: Early tissue growth appears as a firm, tender lump. This phase occurs most often in infants, teenagers, and with sudden medication changes.
- Chronic phase: After several months, the tissue often becomes firmer due to fibrosis or scar formation. Chronic stage cases are less likely to resolve without intervention.
- Resolution or persistence: In infants and adolescents, tissue frequently resolves on its own. In adults, persistent tissue usually requires definitive treatment.
Understanding the phase and duration helps our surgical team guide treatment decisions and set appropriate expectations. Prompt action during the acute phase can sometimes reverse changes or avoid surgery, while chronic cases are better managed with surgical removal for optimal results.
Diagnosis: How Our Team Evaluates Gynecomastia by Age
A thorough evaluation forms the cornerstone of caring for male breast enlargement at any age. Our surgeon adjusts the assessment based on the patient’s life stage.
Key Steps in Evaluation
Pediatric evaluations focus on growth, development, and possible hormonal disorders. In adolescents, we distinguish normal puberty changes from more serious causes. For adults and seniors, we consider medication history, substance exposure, and chronic diseases.
A step-by-step approach guides this process:
- Medical history: Personal and family history, medication review, and questions about substance use all provide crucial clues.
- Physical exam: Size, consistency, symmetry, and duration of the breast tissue help determine the most likely cause.
- Laboratory testing: Bloodwork may include hormone levels, liver function, thyroid studies, and occasionally genetic tests.
- Imaging: In uncertain cases, ultrasound or mammography may help confirm glandular tissue and rule out rare concerns such as tumors.
This careful approach ensures that treatment addresses the underlying cause, not just the symptom.
When to Consider Treatment for Gynecomastia at Any Age
Monitoring versus Intervention
Our surgical team does not always recommend immediate intervention for all ages, as we carefully evaluate who the ideal candidates are for gynecomastia surgery based on physical and emotional maturity. Infants and most adolescents typically require reassurance and periodic check-ins, as their tissue often resolves without action.
However, our practice advises medical or surgical treatment in situations such as:
- No improvement after 1 to 2 years or worsening symptoms
- Severe pain or tenderness
- Emotional distress is dramatically affecting the quality of life
- Underlying medical disease that requires prompt treatment
- Suspicion of breast cancer (exceedingly rare, but important to consider)
The choice between nonsurgical and surgical options depends on both age and the characteristics of the tissue. Early intervention can significantly improve comfort and self-esteem when appropriate.
Treatment Options: How Age Guides Decisions
Gynecomastia therapy varies by patient age, duration of symptoms, and the underlying cause. Both non-surgical and surgical routes offer relief, but not every option suits all ages.
Nonsurgical Treatments
Young patients in the early stages often benefit from conservative management, including observation and, in some cases, medication. Our doctor may recommend waiting and regular check-ins if the tissue appears likely to resolve.
Medications such as selective estrogen receptor modulators or aromatase inhibitors occasionally help in adolescents or adults when detected early. These drugs work best within the first six months of symptom onset. However, medical therapy is far less effective for long-standing or fibrotic tissue, particularly in older adults.
Surgical Options
Surgery becomes the best option when gynecomastia becomes chronic, causes persistent discomfort, or leads to emotional distress. Surgical techniques include liposuction (for fatty tissue), glandular excision, or both. Our surgical team tailors the approach to each patient’s age, the specific types of gynecomastia present, and the individual’s aesthetic goals.
Precision and attention to scar placement ensure a natural appearance appropriate for any stage of life.
Recovery depends more on the extent of the tissue removal and individual healing rates than on age itself. Most patients return to routine activity within days and can resume exercise within a few weeks, following our surgeon’s postoperative plan. Follow-up care ensures the best outcome, built to suit your long-term health.
Differences in the Emotional Impact of Gynecomastia by Age
Gynecomastia affects not only the body but also a patient’s sense of confidence and mental well-being. The emotional effects usually vary by age and developmental stage.
Age-Related Emotional Considerations
- Childhood: Young boys may not notice or understand the physical changes. Parental concerns drive most care.
- Adolescence: This stage brings the deepest emotional impact. Gynecomastia may hinder participation in sports or social life and provoke teasing or embarrassment.
- Adulthood: Men often report frustration, mild embarrassment, or worry about their appearance during intimacy.
- Older age: Gynecomastia may be misunderstood or overshadowed by other health concerns, but it can still affect confidence and self-image.
At every age, feelings about the body are valid, and compassionate care from our team helps address emotional needs alongside medical treatment.
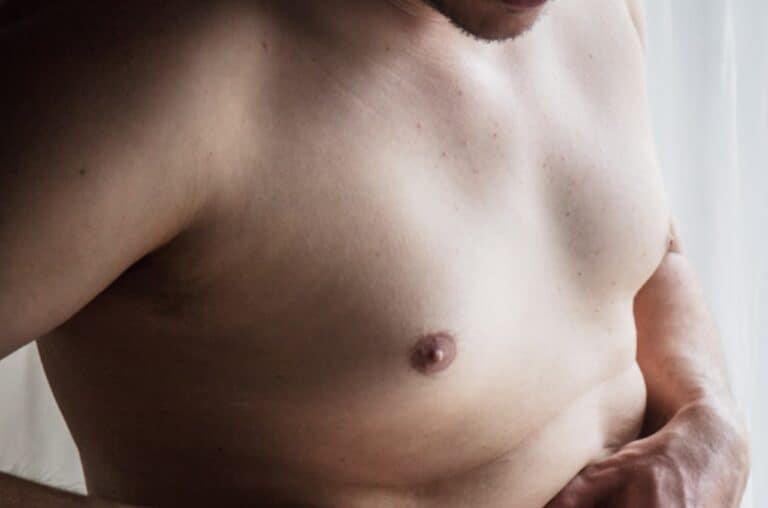

Recurrence and Long-Term Outlook by Age
Gynecomastia generally responds well to targeted therapy for the underlying cause. However, the risk of recurrence depends on a few key factors.
Factors Affecting Recurrence
- Persistent hormone imbalance: Untreated hormonal disorders will likely produce recurrent tissue.
- Medication re-exposure: Restarting a medication associated with gynecomastia can trigger it again at any age.
- Incomplete removal: When surgery leaves behind residual glandular tissue, a small lump may reappear.
Our team at the New Jersey Gynecomastia Center works carefully to treat underlying triggers and to ensure complete, lasting removal of unwanted tissue when surgery becomes necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions about Gynecomastia by Age
Many patients and parents have similar concerns when navigating this diagnosis.
Taking the Next Step toward Relief
Understanding how age influences the cause, appearance, and treatment of gynecomastia equips patients and families to make informed decisions. From infancy through senior years, our team at the New Jersey Gynecomastia Center is dedicated to identifying the best solutions for every stage of life.
The sooner you reach out for evaluation, the more options remain for resolving both physical symptoms and emotional discomfort. Our surgeon combines compassion, technical skill, and a personalized approach to ensure every patient receives age-appropriate care.
If you or someone you care about is noticing breast tissue changes, scheduling a consultation can set your mind at ease. Contact the New Jersey Gynecomastia Center today and take an empowered step forward.